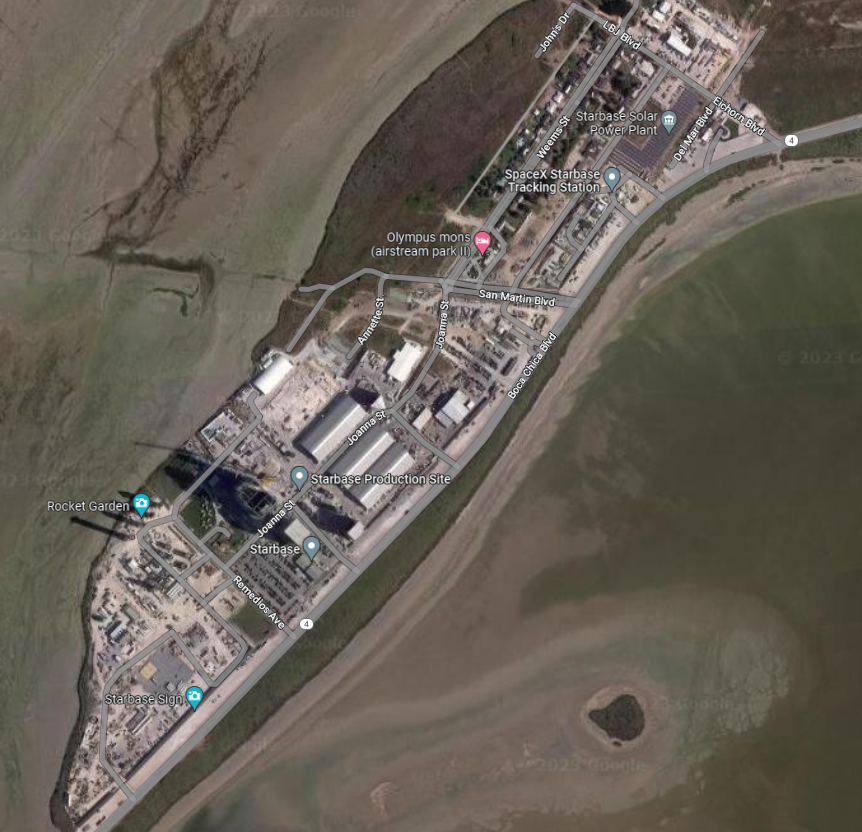
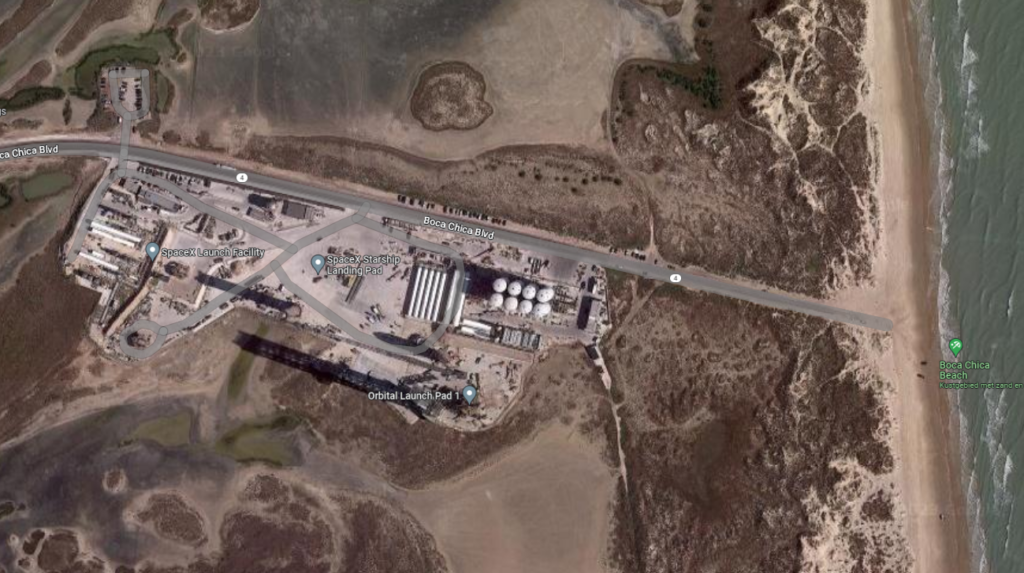
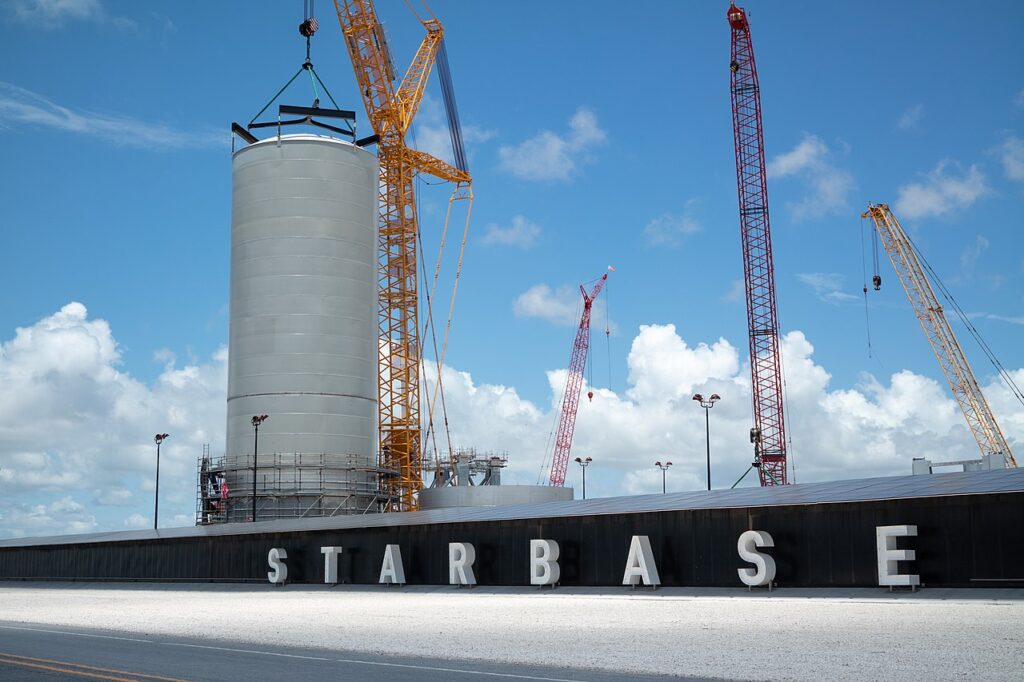
Gerelateerde berichten
Aerospace history
Aerospace history Space dashboard Spaceflight milestones (1880-1961) 00-00-1880 Articles by Tsjolkowsky (1857-1935). 00-00-1923 Articles by Oberth (1894-1989). 16-03-1926 First liquid-fueled rocket by Goddard (1882-1945). Reached 13 meters. 00-00-1932 Gyroscopic rocket by Goddard (1882-1945). 00-00-1937 V1 and V2 by Wernher von…
Astrobotic Technology
Astrobotic Technology Peregrine Missions Lunar lander. Commercial. ULA 08-01-2024 Launch Peregrine with first flight of a Vulcan Centaur (ULA). Kennedy Space Center (KSC). ULA is Boeing and Lockheed Martin). Peregrine Mission One 08-01-2024 Peregrine Lunar Lander (Astrobotic Technology). 08-01-2024 Launch…