Artemis Orion components
- Orion Crew Module (CM): Four astronauts, cargo, from launch to landing, the only part that lands back on Earth. 10,387 kg.
- Orion Crew Module Adaptor (CMA): Connects electrical, data and fluid systems between the main modules, contains electronic equipment for communications, power and control.
- Orion Service Module (SM): Provides electricity, propulsion, air and water. 15,461 kg. SM components:
- European Service Module (ESM).
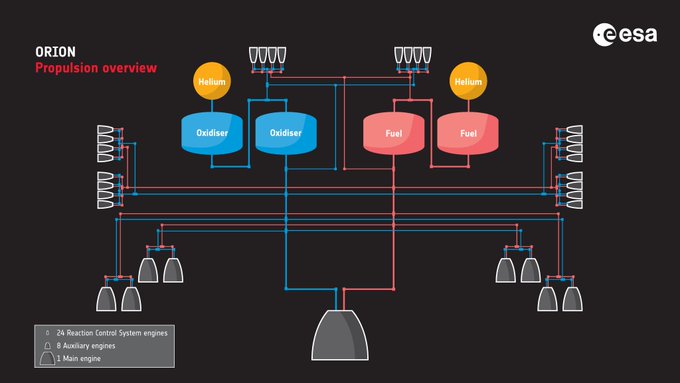
- Propulsion: 33 engines, 3 types. 4 tanks with 8000 litres of fuel.
- Thermal control system: Heater and coolant (6 radiators outside the SM).
- Consumables: Air and water (for 6 astronauts on a 20-day mission).
- Solar Arrays: Turn on 2 axes to remain aligned with the Sun. 4 arrays.
- Chassis structure: Holds everything together, absorbs vibrations, covered with Kevlar.
- Avionics: Computers control all aspects of the SM: Propulsion, water, electronics and temperature.
- Three abort scenario using the SM:
- Untargeted abort splashdown,
- Targeted abort splashdown,
- Ascent abort to orbit.
Orion (officially Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle or Orion MPCV) is a partially reusable crewed spacecraft to be used in NASA’s Artemis program. The spacecraft consists of a Crew Module (CM) space capsule designed by Lockheed Martin and the European Service Module (ESM) manufactured by Airbus Defence and Space. Capable of supporting a crew of six beyond low Earth orbit, Orion can last up to 21 days undocked and up to six months docked. It is equipped with solar panels, an automated docking system, and glass cockpit interfaces modeled after those used in the Boeing 787 Dreamliner. A single AJ10 engine provides the spacecraft’s primary propulsion, while eight R-4D-11 engines, and six pods of custom reaction control system engines developed by Airbus, provide the spacecraft’s secondary propulsion. Although compatible with other launch vehicles, Orion is primarily intended to launch atop a Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, with a tower launch escape system.
ABC of the European Service Module (ESM, SM, Orion Service Module)
| Acronym | Meaning | Explanation |
| AA | Ascent Abort | An Ascent Abort would occur if during the 8 minutes from ignition an Artemis launch is cancelled. The Launch Abort System above Orion can fire and propel the capsule and crew to safety. Later in the launch the European Service Module can also kick in for an ascent abort in three scenarios. |
| AI&T | Assembly, Integration, and Testing | The full process of putting all the parts for Orion together and testing them to ensure they work as planned. |
| APU | Auxiliary Power Unit | A power supply for the spacecraft when on Earth for testing |
| ASEU | Aft Skirt Electrical Umbilical | The electrical systems at the ‘bottom’ of the Orion spacecraft |
| ATLO | Assembly, Test, and Launch Operations | The last assembly and testing before launch focussing on stacking the spacecraft in the rocket. |
| ATP | Authority to Proceed | At specific moments during the assembly of the rocket and spacecraft after testing the teams convene to assess the current situation and confirm continuation of the plan |
| BFS | Backup Flight System | All critical hardware has backups, many have multiple backups for safety. The Backup Flight System is a computer that activates if the main flight system fails. |
| C&DH | Command and Data Handling | The process of sending commands and data between the systems that make up Orion. |
| C/O | Check Out | Testing elements of the spacecraft after assembly |
| CAA | Crew Access Arm | The bridge extension from the launch tower that allows astronauts and technicians access to the Orion spacecraft once it is ready rolled out and ready for launch. |
| CM | Crew Module | The part of Orion where the astronauts are during flight. |
| CMA | Crew Module Adapter | The part of Orion that connects the Crew Module to the European Service Module. Together with the European Service Module, the two make up the Orion Service Module. |
| CMASS | Crew Module Ammonia Servicing Subsystem | The central heating for Orion, using ammonia pumped through radiators to regulate temperature. |
| CS | Core Stage | The main stage of the rocket, for SLS this is the big orange fuel tank two side boosters and motors. |
| CSM | Crew and Service Module | The complete Orion spacecraft. |
| CSS | Consumable Storage System | The tanks that hold the fuel, air and water. |
| CT | Crawler Transporter | The huge machine that transports the rocket and Orion to the launchpad. |
| DCR | Design Certification Review | The moment when a design for the spacecraft or element is analysed and approved. |
| DFAT | Direct Field Acoustics Test | A test where the vibrations of launch are simulated with loudspeakers. |
| DRI | Distant Retrograde Insertion | One of the four main engine burns that the European Service Module will initiate on Artemis I. The Distant Retrograde Insertion is initiated to stay put the spacecraft in Moon orbit. |
| DRD | Distant Retrograde Departure | One of the four main engine burns that the European Service Module will initiate on Artemis I. The Distant Retrograde Departure is initiated to leave the Moon’s orbit and start the voyage home. |
| ECLSS | Environmental Control and Life Support System | The complete system that keeps astronauts alive in space: temperature control, atmosphere, air to breathe, carbon dioxide removal, ventilation and more. Pronounced ‘ecluss’ by astronauts. |
| ECU | Engine Controller Unit | The hardware that directs each engine to fire and for how long. |
| EES | Emergency Egress System | The emergency exit procedure, at the top of an almost 100-m rocket, getting away quickly to safety requires its own procedures and hardware. Astronauts will zip-line to ground and drive an amoured car away. |
| EGS | Exploration Ground Systems | The people and hardware at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center that process rockets and spacecraft until launch. |
| EGSE | Electrical Ground Support Equipment | All electrical equipment that is used to help build and test the spacecraft that does not fly to space. |
| EMI/EMC | Electromagnetic Interference and Electromagnetic Compatibility | Electromagnetic waves that all electrical equipment emits that could interfere with the correct functioning of other equipment. Needs to be tested and controled. |
| ESA | European Space Agency | The space agency responsible for the European Service Module, consisting of 22 Member States. |
| ESD | Exploration Systems Development | Former NASA division responsible for Orion spacecraft. |
| ESM | European Service Module | The powerhouse for Orion providing fuel, water, electricity and propulsion. |
| ESTEC | European Space Research and Technology Centre | Located in Noordwijk, the Netherlands, ESA’s technical heart is where the European Service Module team is based as well as their mission control room. |
| ETE | End to End | The complete process from start to finish. |
| EUS | Exploration Upper Stage | The high-power engine that will propel Orion from Earth orbit to the Moon in future Artemis missions from Artemis IV onwards. It is discarded after use. |
| FAST | Final Assembly and System Test | The hardware used to connect and test the European Service Module and the Crew Module |
| FCAS | Flight Controller Application Software | Software used by mission control to interpret data from the spacecraft |
| FCV | Flow Control Valve | A valve that regulates how much liquid or gas is let through, used for the engines and life support systems. |
| FDIR | Fault Detection Isolation& Recovery | Pinpointing an error in the system and finding a work-around |
| FEE | Front-End Equipment | Used in Orion for the hardware interfaces that simulate aspects of spaceflight, used for the solar array simulators in particular. |
| FM | Flight Model | The version of the spacecraft hardware that actually flies to space, as opposed to testing models. |
| FMA | Final Mission Analysis | The last analysis of a mission plan |
| FPGA | Field-Programmable Gate Array | An integrated circuit that is configured after manufacturing and are used everywhere, including on the European Service Modules |
| FRAC | Flight Readiness Analysis Cycle | Mission-specific information, such as mass properties, Booster burn rates, and launch window, to determine performance of the system. |
| FRR | Flight Readiness Review | The final review of hardware integration giving the thumbs-up for spaceflight |
| FSW | Flight Software | The computer programmes that control the spacecraft during its mission |
| FWD | Forward | The front, in Orion’s case this is the nose cone of the Crew Module. |
| GFAS | Ground/Flight Application Software | The computer programmes used on Earth to run the mission |
| GFAST | Ground/Flight Application Software Team | The people who use and make the computer programmes used on Earth to run the mission |
| GHe | Gaseous Helium | Helium gas (the lightest gas in the Universe) when not in liquid or solid form. In the European Service Module helium is used to push fuel through the guel tanks |
| GLS | Ground Launch Sequencer | The countdown to launch and sequence of events to the run-up |
| GN2 | Gaseous Nitrogen | Nitrogen gas when not in liquid or solid form. Nitrogen makes up roughly 70% of our atmosphere so humans breathe it in at all time. The European Service Module stores nitrogen in tanks to mix with oxygen for astronauts to breathe. |
| GNC | Guidance, Navigation, and Control | The complete system that tells Orion where it is, where it should go, and how to do it |
| GO2 | Gaseous Oxygen | Oxygen when not in liquid or solid form. Nitrogen makes up roughly 70% of our atmosphere so humans breathe it in at all time. The European Service Module stores nitrogen in tanks to mix with oxygen for astronauts to breathe. |
| GR&A | Ground Rules and Assumptions | A large list of rules and procedures used during the mission. Think, “if this happens at this moment then we will assume it is because this happened” |
| GRAS | Green Run Application Software | Computer programmes used to run and analyse the test-firing of the Artemis SLS rocket core stage |
| GRC | Glenn Research Center | NASA technical expertise centre in Ohio, USA, where the European Service Module test article was put to its paces |
| GSE | Ground Support Equipment | All the equipment used on Earth to help build and test Orion, think tools, trolleys to hold the tools but also diagnostic equipment and more |
| HB | High Bay | A large building that can hold a complete spacecraft or rocket for testing or integration |
| HOTH | Houston Orion Test Hardware | Equipment used to simulate an Orion mission to train mission controllers at NASA’s |
| HW | Hardware | Equipment, anything that you can touch that helps Orion go to space |
| ICPS | Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage | The large engine that boosts Orion to the Moon from Earth orbit and is discarded after use |
| ICPSU | Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage Umbilical | The electronic connection between the large engine that boosts Orion to the Moon from Earth orbit and is discarded after use |
| IPO | Initial Power On | The first time the spacecraft is provided with electrical power and switched on |
| ITL | Integrated Test Laboratory | Located at Lockheed Martin’s Denver, Colorado, USA, site the Integrated Test Laboratory is where the software is tested for Orion |
| JICB | Joint Integrated Control Board | Board tri-chaired by the chief engineers from each programme (Orion, SLS, EGS), charged with maintaining the cross-programme technical baseline |
| JM | Jettison Motor | An engine that is discarded during the mission, either from the rocket or in the first Artemis missions the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage that is discarded after it boosts Orion to the Moon. |
| KSC | Kennedy Space Center | NASA centre in Florida, USA, where Orion has its final checkout, integration, placing on the rocket and launch |
| LAS | Launch Abort System | The cone at the top of the rocket that can propel the Orion spacecraft away to safety if needed during launch |
| LCC | Launch Commit Criteria | The minimum situation required for a GO for launch, think wind speeds, weather, orbits etc. |
| LETF | Launch Equipment Test Facility | Located at NASA’s Kennedy Space Centre this area allows technicians to test hardware before liftoff |
| LH2 | Liquid Hydrogen | Hydrogen (the lightest gas in the Universe) when not in gaseous or solid form. The gas occurs naturally as two hydrogen atoms bonded, hence the 2 in the abbreviation. |
| LN2 | Liquid Nitrogen | Nitrogen when not in gaseous or solid form. Nitrogen oocurs naturally as two nitrogen atoms bonded, hence the 2 in the abbreviation. In the European Service Module nitrogen is stored as a liquid in tanks and mixed with oxygen to create a breathable atmosphere for astronauts. |
| LO2 | Liquid Oxygen | Oxygen when not in gaseous or solid form. Occurs naturally as two oxygen atoms bonded, hence the 2 in the abbreviation. In the European Service Module nitrogen is stored as a liquid in tanks and mixed with oxygen to create a breathable atmosphere for astronauts. |
| LOX | Liquid Oxygen | Nitrogen when not in gaseous or solid form. In the European Service Module nitrogen is stored as a liquid in tanks and mixed with oxygen to create a breathable atmosphere for astronauts. |
| LVSA | Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter | The hardware that connects the rocket to the spacecraft and is discarded after separation. |
| MAF | Michoud Assembly Facility | NASA facility that is part of the Marshall Space Flicht Center, New Orleans, USA, where the Artemis rocket is built. |
| ML | Mobile Launcher | The machine that carries the Artemis rocket and spacecraft to the launchpad, also known as the crawler |
| MPPF | Multi-Payload Processing Facility | A building where many different types of spacecraft or space hardware can be prepared for launch |
| MPS | Main Propulsion System | The large engine or engines in a rocket or spacecraft |
| MSFC | Marshall Space Flight Center | NASA centre in New Orleans, USA, where the Artemis rocket is built |
| NASA | National Aeronautics and Space Administration | The civil space agency for the United States of America and responsible for Artemis and the Orion spacecraft. |
| NDE | Nondestructive Evaluation | A test to see if something works and will not break without actually pushing it beyond its limits and breaking it. |
| O&C | Operations and Checkout | The process of assembling Orion and checking it will work |
| O/D | On Dock | When a spacecraft is not flying, before launch |
| OGV | Ogive Panel | Panels outside the Crew Module that protect it during launch |
| OM | Orbital Manoeuvres | Changes in orientation and course performed by the spacecraft. |
| OMRS | Operations and Maintenance Requirements and Specifications | The list of what is needed when working on the spacecraft and keeping it in good condition before flight. |
| OMS-E | Orbital Maneuvering System Engine | The main engine for Orion is a repurposed Space Shuttle engine that was called OMS-E as ot was used to move once in Earth orbit |
| OPF | Outbound Powered Flyby | One of the four main engine burns that the European Service Module will initiate on Artemis I. The Outbound Powered Flyby is initiated on first approach to the Moon. |
| OSA | Orion Stage Adapter | The connecting hardware between the Orion spacecraft and its booster engine the ICPS |
| OTC | Outbound Trajectory Corrections | Thruster fires performed by the European Service Module with minor course corrections on the way to the Moon. |
| OTP | Orion Transportation Pallet | Hardware used to transport Orion when on Earth |
| PBS | Plum Brook Station | A facility that is part of NASA’s Glenn Research Centre where spacecraft are tested, including Orion. |
| PCDU | Power Control Distribution Unit | The hardware that controls how much of the electricity generated by the solar panels goes to each component. |
| PDU | Power Distribution Unit | The hardware that controls how much of the electricity generated by the solar panels goes to each component. |
| PLI | Propellant Liner Insulation | The protective compound |
| PM | Program Manager | The head of a programme, in this case responsible for building the spacecraft (components) |
| PPE | Power and Propulsion Element | The first module for the lunar Gateway that will orbit the Moon and be visited by Orion |
| PPS | Propulsion Sub System | The complete system for propulsion: from fuel tanks to fuel lines and the engines. |
| PRA | Probabilistic Risk Assessment | A method to analyse and report on how likely something will happen in the domain of engineering and hardware |
| PRM | Perigee Raising Manoeuvre | A boost given by the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage to raise Orion’s orbit around Earth after launch. |
| Proof cell | Proof Pressure Cell | The Proof Pressure Cell at NASA’s Operations and Checkout building in Kennedy Space Center uses helium gas that is piped through newly-welded joints at high pressure to test their effectiveness. If the welds do not leak under increased pressure then they are fit to fly and can withstand the forces of launch and spaceflight. |
| QD | Quick Disconnect | Connectors used to provide fast and easy connection and disconnection of fluid lines |
| QM | Qualification Motor | An engine used to test and ensure the real thing will work correctly once in space |
| RCS | Reaction Control System | The name for the 24 Airbus engines used to orient Orion |
| RPF | Return Powered Flyby | One of the four main engine burns that the European Service Module will initiate on Artemis I. The Return Powered Flyby is initiated to start the return to Earth. |
| RTC | Return Trajectory Corrections | Thruster fires performed by the European Service Module with minor course corrections on the way back to Earth from the Moon. |
| SAR | System Acceptance Review | NASA review to evaluate at the end of the integration process and before integration with SLS the Orion spacecraft and related systems for their ability to fly into space, and getting to the Moon |
| SAW | Solar Array Wings | The four solar panel wings that generate power for the European Service Module |
| SCAPE | Self-Contained Atmospheric Protection Ensemble | The suits worn by technicians when fueling a rocket or spacecraft to protect them from hazardous fuel leaks |
| SCCS | Spaceport Command and Control System | The system used to send commands to the rocket before launch |
| SE&I | Systems Engineering and Integration | Disciplined approach for the definition, implementation, integration and operations of a system |
| SIL | System Integration Lab | Avionics and Software testing facility for the SLS established at Marshall (MSFC) which demonstrates real-time flight control of the launch vehicle during ascent. |
| SITF | Software Integration Testing Facility | Avionics and Software testing facility for the SLS established at Marshall (MSFC) which integrates and tests software specifically for the SLS Core/Upper Stage avionics system |
| SLS | Space Launch System | The Artemis rocket |
| SM | Service Module | The European Service Module including Crew Module Adapter |
| SSC | Stennis Space Center | NASA centre where the Artemis rocket is built and tested. |
| STA | Structural Test Article | A version of a spacecraft that is similar in weight and structure but does not include all the components. Used for testing. |
| SW | Software | Yes, one word can also be abbreviated in spaceflight! |
| TCS | Thermal Control System | The hardware and software that are used to keep Orion and the European Service Module operating at a cozy temperature. |
| TCU | Thermal Control Unit | Hardware used to control the temperature in Orion. |
| TLI | Trans Lunar Injection | A boost from the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage to send Orion off to the Moon from Earth’s orbit. |
| TLM | Telemetry | Data sent to ground control during flight. |
| TPS | Thermal Protection System | The protective covers and raditors used to keep Orion at the correct temperature |
| TRR | Test Readiness Review | A review to see if the hardware is ready for testing |
| TSMU | Tail Service Mast Umbilical | Provides liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen fluid lines and electrical cable connections to the SLS core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations |
| TVC | Thrust Vector Control | The control mechanisms for the engine power. |
| V&V | Verification and Validation | Checking and confirming everything works. |
| VAB | Vehicle Assembly Building | The building at NASA Kennedy Space Center where the rocket is assembled and the spacecraft integrated. |
| VAC | Vertical Assembly Center | Welding facility at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, USA. |
| WDR | Wet Dress Rehearsal | A full-scale test of the rocket where fuel is pumped into the tanks and all aspects of the launch countdown are done until just a few minutes before lift-off. The big final test before a launch. |
Footnote
- Sources: Aerospace dashboard, funkystuff.org
- Outgoing: NASA
- Keywords: